Located in Manhattan, the New York City Archaeological Repository houses a number archaeology collections, recovered from various seventeenth, eighteenth and nineteenth century contexts, including sites in Manhattan, Staten Island and the Bronx. Some of the earliest artifacts date from the late 1600s, just after the British seized New Amsterdam from the Dutch in 1664, renaming it New York City. You might discover items like a colonial bayonet, a 200-year-old douche, and items that show the earliest contributions of women in New York City.
The city’s various immigrants may have even once owned many of these objects, especially those dating from the eighteenth century, such as immigrants from the Netherlands, England, France and Germany, as well as indentured servants and African-American slaves. But an important aspect found in some of these collections is the existence of New York City’s local early household pottery industry.
The manufacture and availability of utilitarian red earthenware in New York City before and after the Revolutionary War is a subject that is likely not as well known today as the local stoneware industry, which was established in Manhattan by the Crolius and Remmey families, as early as the late 1720s and 1730s. Although, red earthenware was actually the original source of domestic household pottery manufactured in the city, later being superseded by stoneware, especially in the nineteenth century.
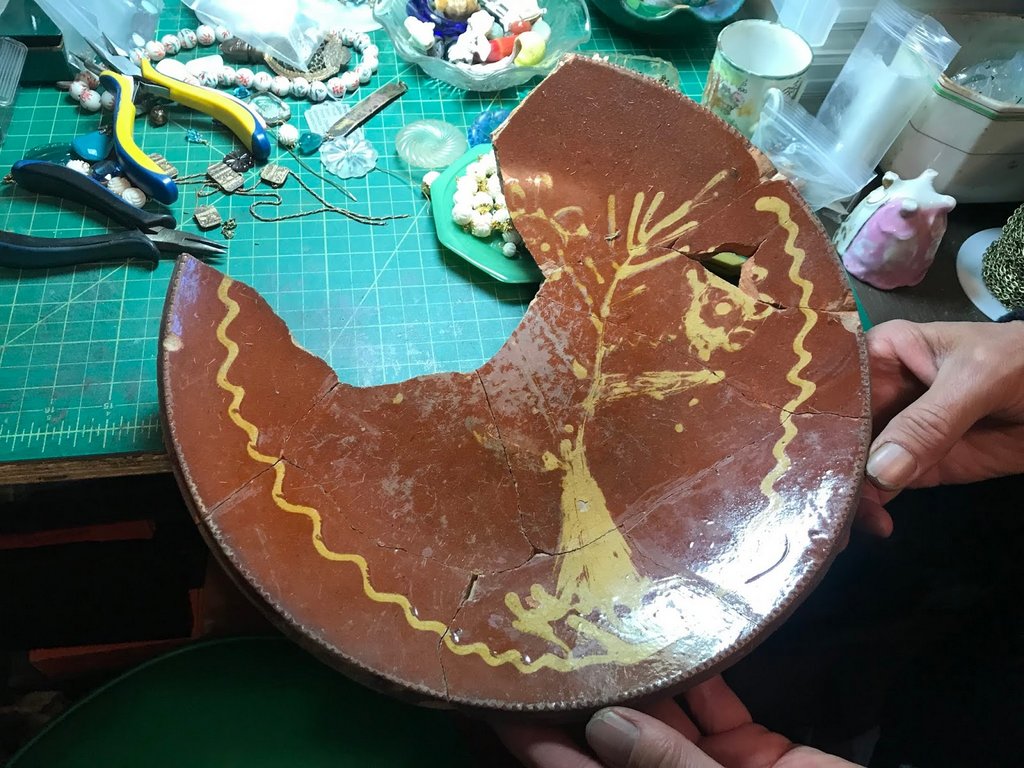 Nineteenth century slip-decorated red earthenware plate recovered in New York City, possibly made in New Jersey. Courtesy: Maribelle Costes and Scott Jordan
Nineteenth century slip-decorated red earthenware plate recovered in New York City, possibly made in New Jersey. Courtesy: Maribelle Costes and Scott Jordan
The production of red earthenware in Manhattan is thought to have begun with Dirck Claesen (circa 1630-1686), a migrant Dutch potter based in the original New Amsterdam settlement. He employed Anthony Dirksen, likely also as a potter. It has been reported that there were only five potters involved with production in the city in the seventeenth century because of burgher rights, which limited the number of potters.
However, by the turn of the eighteenth century, other red earthenware potters began to arrive in Manhattan. Some of the names associated with this Colonial business include John Euwatse, Ewout Euwatse, Dirck Benson, Sampson Benson, and an English potter, John DeWilde. Most of this production likely resembled objects that were familiar to them in their home country, and as a result, it is difficult to differentiate what may have been made locally in comparison to the imported Dutch pottery, often found in Colonial archaeological sites in Manhattan kept in the city’s archaeological repository.
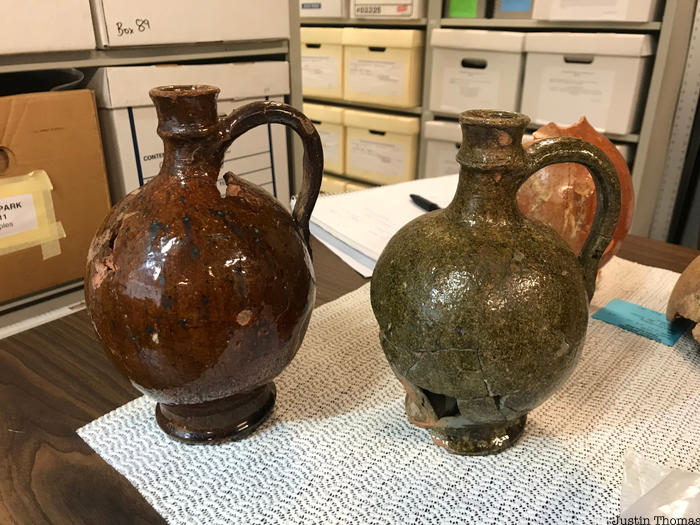 Red earthenware jugs recovered from the Stadt Huys Block Site in Manhattan at the location of the Sir Francis Lovelace (ca. 1621-1675) tavern within a circa 1670-1706 archaeological context. The jugs are thought to have been locally made, modeled after Dutch production, and might have originally held locally brewed ale or cider.
Red earthenware jugs recovered from the Stadt Huys Block Site in Manhattan at the location of the Sir Francis Lovelace (ca. 1621-1675) tavern within a circa 1670-1706 archaeological context. The jugs are thought to have been locally made, modeled after Dutch production, and might have originally held locally brewed ale or cider.
Among the wares thought to have been locally made during this period are five red earthenware jugs, similar to European stoneware or tin glazed forms, which were recovered in 1979-1980, when archaeologists excavated the site of Stadt Huys Block in Manhattan. This was the location of the city’s first town hall, built circa 1641. While the remains of the original building were not recovered, archaeologists did find the foundation of a tavern built by New York City’s second English governor, Sir Francis Lovelace (circa 1621-1675).
The tavern was built about 1670 and was in operation until around 1706. Archaeologists described the brown- and green-glazed jugs as locally made, possibly from the same potter’s business, and modeled after Dutch production. They also suggested that the jugs might have originally held locally brewed ale or cider. A notable red earthenware mug manufactured with a coiled handle terminal was also recovered from this site.
 Red earthenware mug recovered from the Stadt Huys Block Site in Manhattan, which was manufactured with a coiled handle terminal.
Red earthenware mug recovered from the Stadt Huys Block Site in Manhattan, which was manufactured with a coiled handle terminal.
Another significant local potter was Jonathan Durell (business active 1753-1806), who had reportedly come from Philadelphia, where he likely learned to manufacture red earthenware. A potter of the same surname, Philip Durell operated just outside of New York City in Elizabethtown, New Jersey; he was active by 1781, and an example of his sgraffito production is owned by the Newark Museum in New Jersey, inscribed with the date, “October 27th 1793.”
John Campbell and his sons John T. and Thomas I., and his brother, Thomas also operated their own family business in Manhattan from the late 1750s to the early 1800s. In addition, some of this production may survive above ground today, but how to determine what they actually made is challenging because the site of this business, as well as others is long gone, leaving a great uncertainty of how this local production actually appeared.
It is likely that some production from Durell and the Campbells is represented within eighteenth century contexts found in the city’s archaeology collections, but there needs to be more evidence to definitively attribute any given artifact to a specific business or potter.
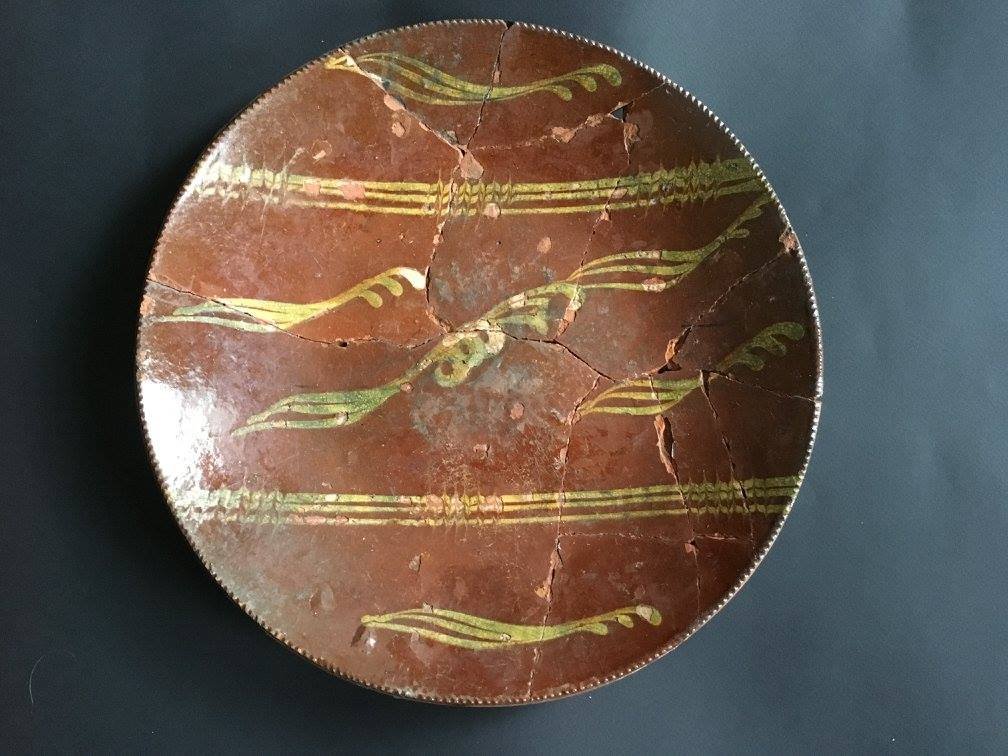 Nineteenth century slip-decorated red earthenware plate likely from New Jersey, Long Island or Norwalk, CT, although Absalom Day manufactured similar styles of slip in Norwalk. Recovered from a privy in New York City. Courtesy: Maribelle Costes and Scott Jordan.
Nineteenth century slip-decorated red earthenware plate likely from New Jersey, Long Island or Norwalk, CT, although Absalom Day manufactured similar styles of slip in Norwalk. Recovered from a privy in New York City. Courtesy: Maribelle Costes and Scott Jordan.
However, New York City presented new opportunities after the American Revolution, as the city’s population began to outgrow the abilities of the local pottery industry. The city’s population was around 60,000 people in 1800, but over the next 100 years, it expanded to 3.4 million people, growing to be America’s largest city. And like the city’s diverse population, potters located to the north, east and south began to regularly export their production to merchants located all over the city, creating a distinct selection of wares throughout one of America’s most important ports in the 1800s.
Among the notable potteries, exporting their wares to the city was a business located along the Hackensack River in River Edge, Bergen County, New Jersey, established by Henry Jacob Van Saun (d. 1829) about 1811. Although, the wares from this business that are most recognizable today are those that were made by George Wolfkiel (1805-1867), who was born in Franklin Township, Chester County, Pennsylvania. He was likely a Pennsylvania trained potter before he arrived in River Edge sometime around 1830.
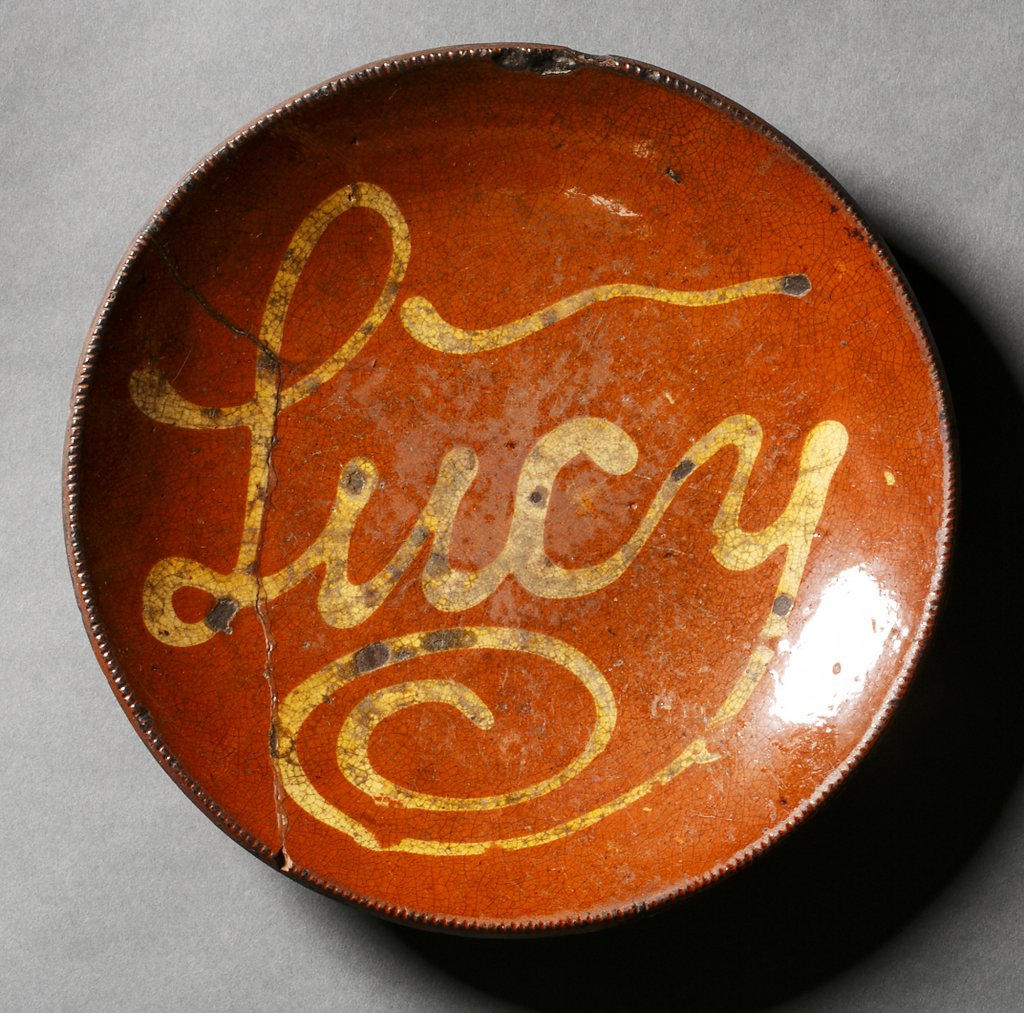 Nineteenth century slip-script red earthenware dish, “Lucy,” made by George Wolfkiel in River Edge, New Jersey. This dish retains a history ownership on Staten Island. Wolfkiel is known for his distinctive curly “Y.” Courtesy: Staten Island Historical Society.
Nineteenth century slip-script red earthenware dish, “Lucy,” made by George Wolfkiel in River Edge, New Jersey. This dish retains a history ownership on Staten Island. Wolfkiel is known for his distinctive curly “Y.” Courtesy: Staten Island Historical Society.
This type of production has been recovered in Manhattan, but it has also been found in various contexts on Staten Island, including a slip-script dish owned by the Staten Island Historical Society, retaining a history of local ownership, reading “Lucy.” This dish is attributed to Wolfkiel because of a distinctive curly “Y,” a characteristic of Wolfkiel’s production, circa 1830-1867.
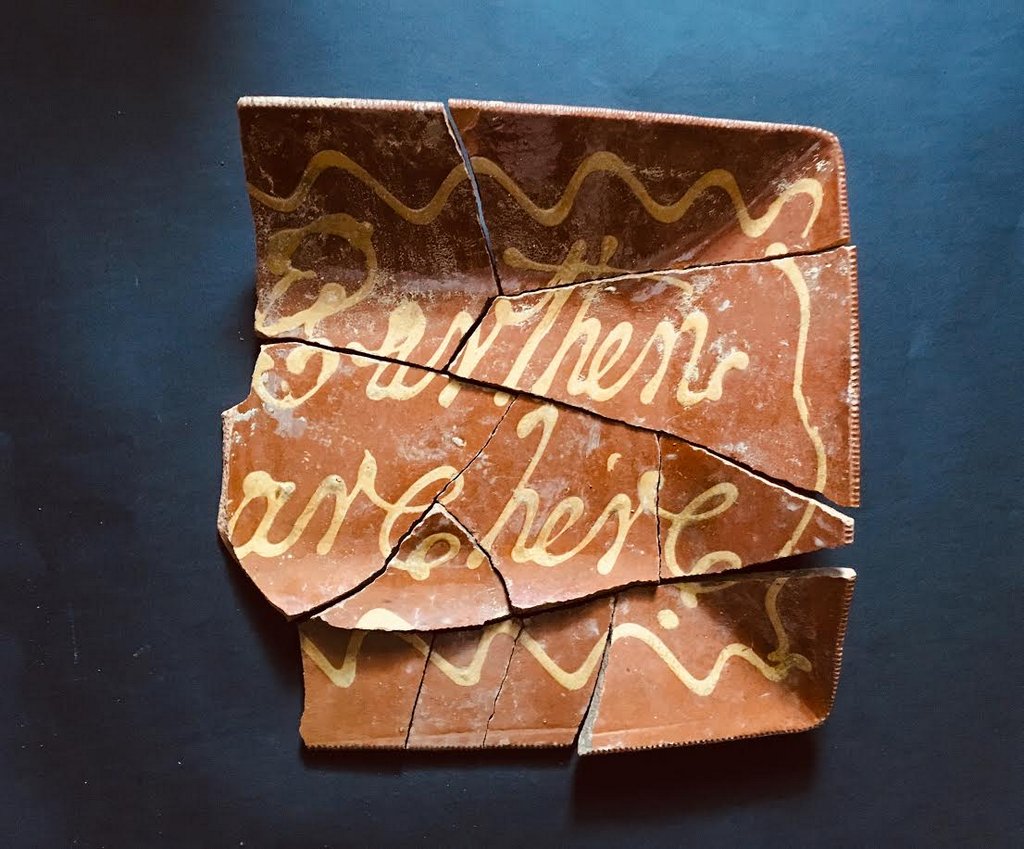 Nineteenth century slip-script red earthenware advertising platter, “Earthen Ware Here,” possibly made by George Wolfkiel in River Edge, New Jersey. The platter was recovered from an 1835-1845 brick-lined privy at 33 Van Duzer Street on Staten Island. Courtesy: Scott Jordan, Maribelle Costes and Dan McGee
Nineteenth century slip-script red earthenware advertising platter, “Earthen Ware Here,” possibly made by George Wolfkiel in River Edge, New Jersey. The platter was recovered from an 1835-1845 brick-lined privy at 33 Van Duzer Street on Staten Island. Courtesy: Scott Jordan, Maribelle Costes and Dan McGee
Two fascinating slip-script red earthenware objects were also recently recovered from a brick-lined privy at 33 Van Duzer Street on Staten Island, where the context of the privy dates between 1835-1845. A merchant probably used one of the objects for storefront advertising, seeing that it reads, “Earthen Ware Here.” However, it does not necessarily indicate the merchant was exclusively a retailer of local earthenware; they probably sold all types of earthenware that was regularly shipped to New York City and the surrounding area in the 1800s.
Interestingly, the style of the slip-script found on this advertising platter is similar to two platters in the collection of the Bergen County Historical Society and the Wadsworth Atheneum Museum of Art in Hartford, Connecticut. These platters are inscribed, “Hard Times in Jersey,” and were made by Wolfkiel.
 Nineteenth century slip-script red earthenware dish, “Good Morning Ladies,” possibly made by John Betts Gregory in Norwalk, Connecticut. The dish was recovered from an 1835-1845 brick-lined privy at 33 Van Duzer Street on Staten Island. Courtesy: Scott Jordan, Maribelle Costes and Dan McGee
Nineteenth century slip-script red earthenware dish, “Good Morning Ladies,” possibly made by John Betts Gregory in Norwalk, Connecticut. The dish was recovered from an 1835-1845 brick-lined privy at 33 Van Duzer Street on Staten Island. Courtesy: Scott Jordan, Maribelle Costes and Dan McGee
The other recovered object reads, “Good Morning Ladies.” The manner of the script on this platter is similar to wares made by John Betts Gregory (1782-1842), who learned his trade from Absalom Day (1770-1843) in Norwalk, Connecticut in the late eighteenth century. Day was a New Jersey trained potter born in Morris County, New Jersey, arriving in Norwalk in 1792. Gregory then left for the Huntington Pottery on Long Island, before he arrived in Clinton, New York, sometime around 1810. Gregory ran a pottery in Clinton for about twenty years. He then returned to Norwalk around 1831, where he produced red earthenware until his death in 1843. The context that this plate was recovered is according to Gregory’s second employment in Norwalk, which makes sense since Norwalk was a major supplier of red earthenware in New York City in the 1800s.
 In the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art is a slip-script dish made in Norwalk that likely shows this industry’s great interest within this market, reading, “New York City,” which is attributed to Asa Edward Smith (1798-1880). Image in public domain.
In the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art is a slip-script dish made in Norwalk that likely shows this industry’s great interest within this market, reading, “New York City,” which is attributed to Asa Edward Smith (1798-1880). Image in public domain.
The industry in Norwalk was established in the eighteenth century, although there was a business that possibly operated as early as the seventeenth century, known as Settler’s Pottery. But production really took off when five businesses were operating, most of which happened in the nineteenth century. Those businesses were known as the Hoyt Pottery, the Day Pottery, the Gregory Pottery, the Quintard Pottery and the Smith Pottery. Asa E. Smith established the Smith Pottery in 1825; production from the Smith Pottery may represent the majority of the wares from Norwalk found in nineteenth century archaeological contexts in New York City today, especially the slip-script wares. The business ceased production sometime around 1887.
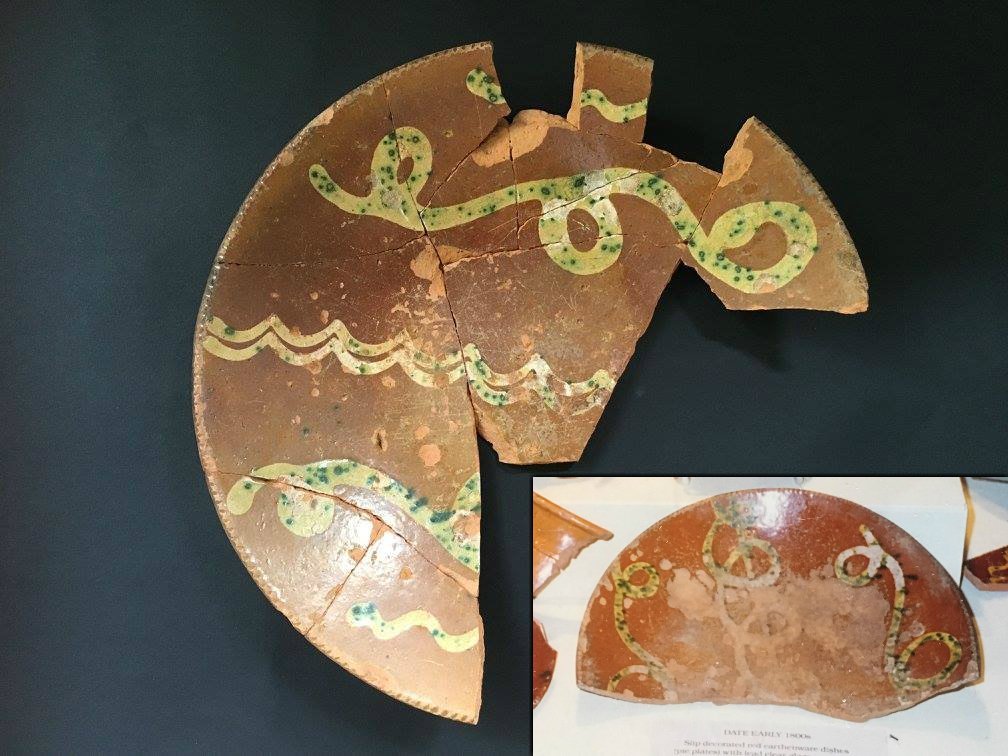 Nineteenth century slip-decorated red earthenware plate attributed to the Huntington Pottery on Long Island. Recovered from a privy in New York City. (Inset photo) Similar nineteenth century slip-decorated plate recovered within an 1840 context on the property of the circa 1730 Suydam House located a few miles from Huntington. Courtesy: Anthony Butera, Jr., Maribelle Costes, Scott Jordan and the Greenlawn-Centerport Historical Association.
Nineteenth century slip-decorated red earthenware plate attributed to the Huntington Pottery on Long Island. Recovered from a privy in New York City. (Inset photo) Similar nineteenth century slip-decorated plate recovered within an 1840 context on the property of the circa 1730 Suydam House located a few miles from Huntington. Courtesy: Anthony Butera, Jr., Maribelle Costes, Scott Jordan and the Greenlawn-Centerport Historical Association.
Other prominent industries that shipped their production to New York City in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries include Philadelphia and the Huntington Pottery on Long Island. The industry in Philadelphia was outstanding and among the most accomplished anywhere in America during this period; production has been recovered from archaeological contexts in the South, throughout the Mid-Atlantic Region and all over the Northeast, demonstrating how prominent this red earthenware industry was, especially in the eighteenth and early nineteenth century. Archaeologists in Manhattan have recovered a variety of Philadelphia wares, and much of this is found in the city’s archaeological repository.
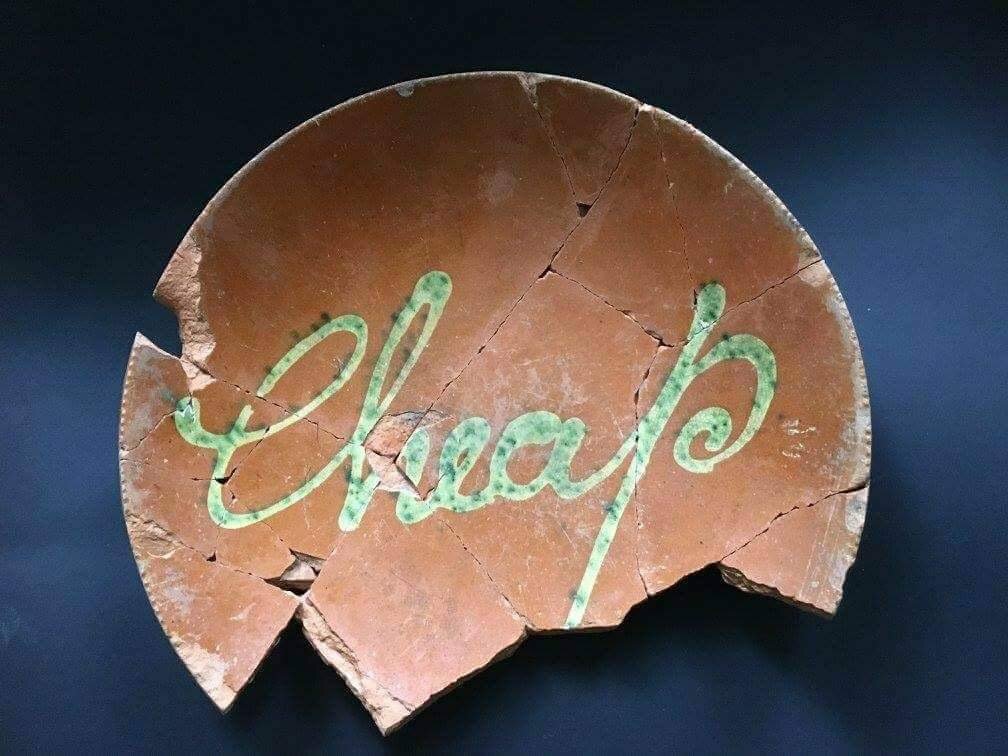 Nineteenth century slip-script red earthenware plate, “Cheap,” likely made at the Huntington Pottery on Long Island. Recovered from a 27 foot privy on Houston and Orchard Streets in Manhattan within a circa 1820s-1830s context. Courtesy: Maribelle Costes and Scott Jordan
Nineteenth century slip-script red earthenware plate, “Cheap,” likely made at the Huntington Pottery on Long Island. Recovered from a 27 foot privy on Houston and Orchard Streets in Manhattan within a circa 1820s-1830s context. Courtesy: Maribelle Costes and Scott Jordan
The Huntington Pottery was an economic force on Long Island in the nineteenth century, providing the island and the city with a wide variety of household wares. Although, the most prevalent today are the wares that were decorated with slip, often applied in stamped designs or script. This type of production has been found in various contexts in New York City, especially in Manhattan, where some of the recovered script reads, “For Nancy,” “Cheap,” “Mary,” and “Picky.”
 Nineteenth century slip-script red earthenware plate, “For Nancy,” likely made at the Huntington Pottery on Long Island. Recovered from a privy in New York City. Courtesy: Maribelle Costes and Scott Jordan.
Nineteenth century slip-script red earthenware plate, “For Nancy,” likely made at the Huntington Pottery on Long Island. Recovered from a privy in New York City. Courtesy: Maribelle Costes and Scott Jordan.
Some may even consider Huntington’s wares from the early to mid-1800s, as complimentary to what was made in Norwalk during this period, seeing there are similarities in forms, glazes and some styles of slip. The New York City marketplace is also, where production from both of these industries eventually met. It would certainly be interesting to learn if the Norwalk and Huntington production was branded separately in the city or if it was just sold as Earthen Ware, such as indicated on the advertising platter recovered on Staten Island.
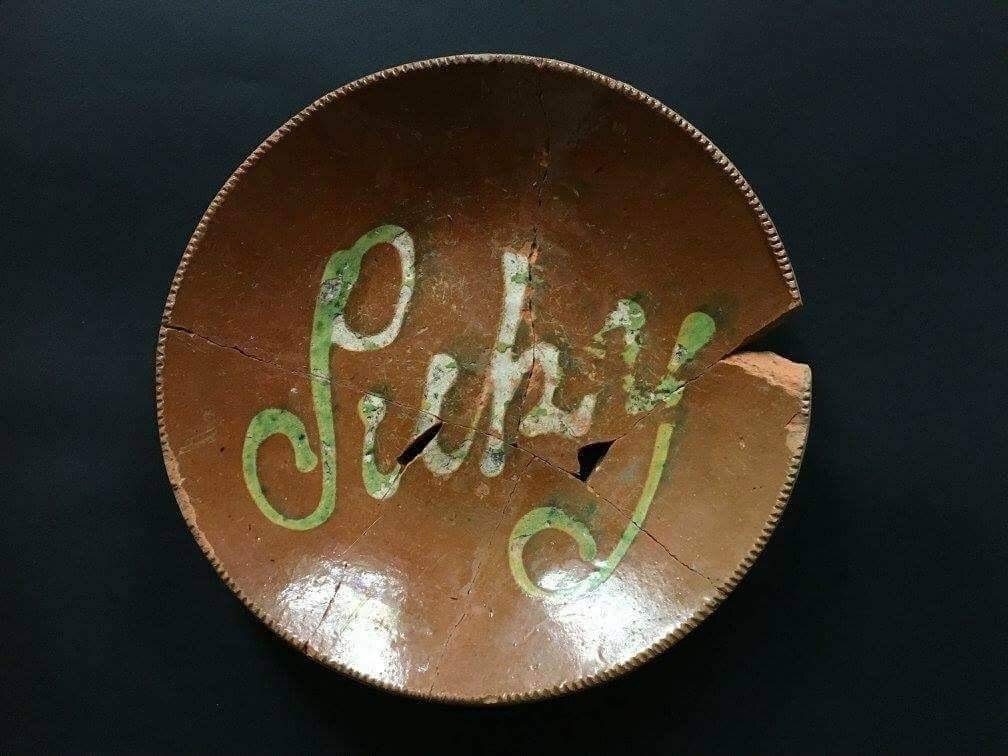 Nineteenth century slip-script red earthenware plate, “Picky,” likely made at the Huntington Pottery on Long Island. Recovered from a 27 foot privy on Houston and Orchard Streets in Manhattan within a circa 1820s-1830s context. Courtesy: Maribelle Costes and Scott Jordan
Nineteenth century slip-script red earthenware plate, “Picky,” likely made at the Huntington Pottery on Long Island. Recovered from a 27 foot privy on Houston and Orchard Streets in Manhattan within a circa 1820s-1830s context. Courtesy: Maribelle Costes and Scott Jordan
There was also a somewhat unknown red earthenware pottery that operated on the eastern end of Long Island in Greenport after 1819, where a lot of the production also incorporated slipware. But I have not yet seen any archaeological evidence to prove this business shipped its production to New York City.
The need for household red earthenware eventually faded in New York City by the late 1800s, but the city’s demand and economic impact helped sustain local potters, small businesses and major industries for nearly 200 years. The wares that were imported even supported merchants, their families, and immigrants and other employees who worked at the docks. The constant demand for utilitarian pottery in the city was a real driving force for the local economy, and while some of this production survives above ground today, the majority of it was discarded years ago, and is represented today in eighteenth and nineteenth century archaeological contexts found beneath the city, as well as artifacts that have already been recovered, now kept at the New York City Archaeological Repository.
Justin W. Thomas regularly writes about early American pottery production for various regional and national publications, as well as posts a variety of pottery related stories on his blog, EarlyAmericanCeramics.com. He has also authored three books about eighteenth and nineteenth century pottery production in Massachusetts including The Beverly Pottery: The Wares of Charles A. Lawrence.
Next, check out 8 highlights of the NYC Archaeological Repository.